This week's case is by Idzi Potters and the Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp. The following object was removed from a furuncular skin lesion in a patient with recent travel to Uganda. Once they were able to keep it still (!), Idzi captured the following photographs demonstrating all of the diagnostic features. What is your identification?
Thursday, December 7, 2023
Sunday, December 3, 2023
Answer to Case 733
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 733: Cordylobia anthropophaga, myiasis causing fly larva.
Florida Fan painted an accurate picture of this parasite with his vivid description: "The mango fly, aka Tumbu fly, lays eggs on human clothing hung to dry in the sun. The Man-Eating larvae hatching eats its way into the skin of its prey. The three sinuous slits are definite identification clues. Ironing the clothes dried outdoor kills the eggs and prevent a myasis infection. The video clearly exemplifies the voracious nature of The Beast." Very apt!
The adult female fly also commonly lays her eggs on sandy soil contaminated with urine and feces. The larvae hatch and may remain viable in the soil for 1-2 weeks while seeking a host. Upon contact with a suitable host, the larvae burrow into the skin of the host and develop for 8-12 days. They then emerge from the host and develop into pupae in the environment.
Extracted larvae can be identified based on the characteristics of their posterior spiracules, as well as their general body characteristics. There are several keys available for genus and species-level identification, including this older key from the CDC. Blaine Mathison and I also published a review on arthropod identification which you may find helpful.
Along with this case, Idzi provided some great photos from previous posts for comparison:
Corydylobia rodhaina (Case of the Week 547):
Lastly, I'd encourage you to check out ITM's outstanding new podcast series entitled Transmission. Thanks again to Idzi and ITM for this great case!
Monday, November 27, 2023
Case of the Week 732
Welcome back to all of my US readers from the Thanksgiving holiday. Here is a fun case with the answer embedded - just listen to the audio with the video. Or if you'd prefer, keep the volume down and give your best guess on what you think this is!
This case is donated by Dr. Jessica Lin and her colleague who is field physician in Tanzania. The patient is a 4 year old boy with anal pruritus and history of passing worms from his anus. Several white-tan worms measuring ~5mm long were examined:
Sunday, November 26, 2023
Answer to Case 732
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 732: Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) adult female.
As noted by Florida Fan, "Well, this is a classic situation. Children by nature are very altruistic, sharing their prize possessions (e.g., M&M’s). The asymmetric eggs with a flat side and a convex side are commonly shared in this fashion." The appearance of the eggs is also called planoconvex or "D" shaped. Anonymous mentioned that the extensive uterine reproductive system of the fertilized female worm is often completely filled with with these eggs.
If you watched the video, you could see the movement of the eggs within the uterus, and appreciate the prominent lateral alae (arrows):
Wednesday, November 15, 2023
Case of the Week 731
The following objects were seen in fluid aspirated from a cyst in the liver. Identification?
Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Answer to Case 731
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 731: Echinococcus sp. protoscolex. Hopefully you all got to look at it moving! Given that this is a single liver cyst, it would fit with E. granulosus. Correlation with radiologic and epidemiologic features would be helpful for confirmation.
Here are some of the key diagnostic features:
Thursday, November 9, 2023
Case of the Week 730
This week's case is generously donated by Idzi Potters and the Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp.
The following were seen in used contact lens solution from a young woman with complaints of eye pain and blurry vision. The first two images are taken with light microscopy, and the third with phase-contrast microscopy. What is your diagnosis? Please describe the forms you are seeing.
Wednesday, November 8, 2023
Answer to Case 730
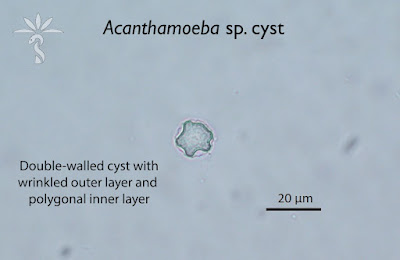
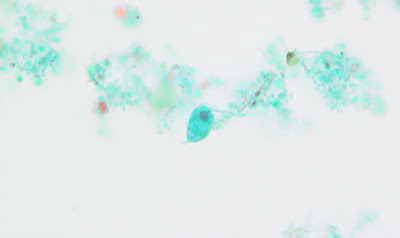
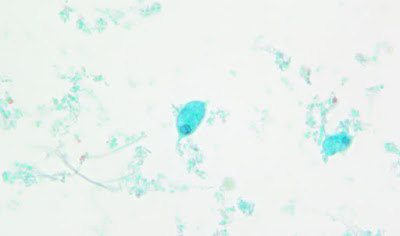
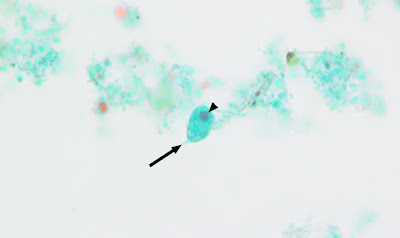
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 730: Acanthamoeba keratitis.
As noted by Anonymous, the pictures are a perfect rendition of the “thorny” Acanthamoeba trophozoite and its polygonal cyst (acanth is New Latin, from Greek akanthos, from akantha thorn, spine). Cysts have 2 layers: a wrinkled outer layer (ectocyst) and inner layer (endocyst) that can be polygonal, spherical, hexagonal, or star-shaped.
Dr. Satishkumar Krishnam further described the trophozoite as "characterized by spine like pseudopodia (acanthopodia)." Chuck Blend noted that it looks like the first few seconds of a new proto-universe forming!
Thanks again to Idzi for this great case!Thursday, November 2, 2023
Case of the Week 729
This week's case was generously donated by Drs. Jacob Rattin, Anisha Misra, and Hannah Wang, and originally identified by Marissa Roberts. The following objects were seen on a trichrome-stained stool specimen and measure approximately 15 micrometers in length. What is your identification?
Wednesday, November 1, 2023
Answer to Case 729
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 729: Trophozoites of Chilomastix mesnili
Below is an answer written by Dr. Jacob Rattin (@EternalStudying):
This non-pathogenic flagellate has pear-shaped trophozoites that are 6 – 24 μm long with a longitudinal spiral groove running along the body (not seen in this specimen). If visualized in a fresh prep, the motility may allow the spiral groove to be seen as the organism turns (see Case 475). The trophozoite has one nucleus (arrowhead), usually at the anterior end, with an eccentric karyosome and a cytostome (oral groove) close by. The posterior end tapers to a point (arrow).
Differentiating C. mesnili trophozoites from other non-pathogenic flagellates such as Enteromonas hominis, Pentatrichomonas hominis, and Retortamonas intestinalis can be quite difficult. Thankfully, these organisms are non-pathogenic. However, the following features may be useful in teasing apart these fun flagellates!
Enteromonas hominis trophozoites measure 5 – 7 µm long with one nucleus and three anterior flagella and one posterior flagellum. It has a single nucleus with a large karyosome. There is no cytostome which helps to differentiate it from C. mesnili.
Retortamonas intestinalis are 4 – 10 µm long with an ovoid trophozoite form with a cytostome at the anterior half that is bordered by a fibril. The single nucleus is at the anterior end and has a small karyosome.
Pentatrichomonas hominis. The trophozoites are pyriform in shape, measuring 6 – 20 µm long. They have five flagella, with four directed anteriorly and a fifth directed posteriorly. The fifth flagellum forms the outer edge of an undulating membrane and projects beyond the posterior. A single nucleus is at the anterior end and contains a small karyosome.
Thanks again to Dr. Rattin for taking on the non-pathogenic flagellates! I'm sure you'll agree that he did an excellent job. Thanks also to the laboratory technologist, Marissa Roberts, who took these photos, and to Dr. Anisha Misra at the Cleveland Clinic for her scientific oversight.
Wednesday, October 11, 2023
Case of the Week 728
This week's case was donated by Drs. Meredith Kavalier, Megan Shaughnessy, and David Cartwright. The patient has a history of treated urothelial cell carcinoma and remote travel to Asia. The cytopathologist was concerned by the presence of the following structures seen in a routine screening urine sample. How would you interpret these findings?
Tuesday, October 10, 2023
Answer to Case 728
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 728: Not a parasite egg; uric acid crystals.
Uric acid crystals are a very convincing mimic of Schistosoma haematobium eggs! They are both found in urine, and they both have a terminal spine. However, there are a number of features that can be used to easily differentiate the two:
- Uric acid crystals vary in size and shape and are often much smaller than S. haematobium eggs. In contrast, S. haematobium eggs are regular in size and shape, and quite large (approximately 150 micrometers in length).
- Uric acid crystals commonly have points on both ends instead of the single 'pinched-off' spine of S. haematobium eggs. They can also have lateral points or take on other shapes.
- There are no internal parasite structures (i.e., miracidium) in uric acid crystals
- Finally, crystals often fracture and break, and may have irregular contours.
Tuesday, September 26, 2023
Case of the Week 727
his week's case was generously donated by Dr. Richard Bradbury. The following structure was seen in a concentrated wet prep of stool. It measures approximately 80 micrometers in diameter. Check out the video to see this structure in multiple planes. Identification?
Monday, September 25, 2023
Answer to Case 727
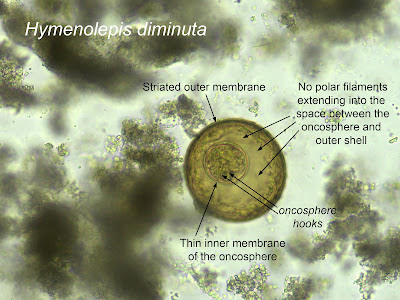
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 727: Hymenolepis diminuta
As noted by Lamia Gala on LinkedIn, "The distance between the outer and the inner shell is large with no polar filaments" which is consistent with H. diminuta. This is in contrast to Rodentolepis (formerly Hymenolepis) nana, which does have polar filaments between the outer and inner shell. H. diminuta is also slightly larger than R. nana, measuring 70-85 micrometers in greatest dimension (compared to 30-50 for R. nana). Florida Fan provided the helpful memory aid that the word "diminuta" is larger in size than "nana", which also applies to their eggs (thanks FF!). Here are some of the key morphologic features:
Thanks again to Dr. Bradbury for donating this lovely case!Monday, September 18, 2023
Case of the Week 726
This weeks case features the following small, oval-shaped, red-staining objects seen in a bronchoalveolar specimen from an immunocompromised patient. The objects measure approximately 2 micrometers long. The stain is a strong trichrome (chromatrope 2R method). Identification? What is the significance of this finding? (CLICK ON IMAGES TO ENLARGE)
Sunday, September 17, 2023
Answer to Case 726
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 726: Microsporidia spores; genus and species not determined
These small spores stain deep red with the chromotrope 2R method and its modifications. They are oval shaped and often have a darker-staining equatorial band in the middle of the spore. Spores of Enterocytozoon bieneusi are very small (0.8 to 1.4 micrometers long), whereas other species such as Encephalitozoon spp., Vittaforma cornea, and Anncaliia algerae are a little larger. Some (e.g., Anncaliia) are up to 4 micrometers long and may be mistaken for small years such as Histoplasma capsulatum (especially because they are focally GMS positive!)
As Dr. Couturier pointed out, microsporidia are not parasites, but fungi (his words: "Not a parasite LOL Get those buggers off this page and send them to the Mycology lab. 😉) . They are obligate intracellular, unicellular, spore-forming eukaryotic organisms comprising more than 220 genera and 1,700 species. Microsporidia itself is NOT a genus and should not be italicized.Tuesday, September 5, 2023
Case of the Week 725
This week's interesting case is generously donated by Dr. Justin Juskewitch. Hopefully all of you have been able to avoid this so far this summer!
The patient is a young girl who developed this very itchy rash about 30 minutes after a swim in a fresh water lake in Maine (Northeastern United States). The rash developed to what is shown below over a period of several hours.
Her two siblings had a similar presentation. All three children had resolution of itching with benadryl, corticosteroid cream, and oatmeal body wash baths over the next few hours, but the rash lasted for 5-7 days.
What is the most likely diagnosis? Is any additional therapy recommended?
Sunday, September 3, 2023
Answer to Case 725
Answer to Parasite Case of the Week 725: Swimmer's itch
As noted by Florida Fan, this is "typical swimmer’s itch, also known by other names depending on the activity of the patient like 'clam digger’s itch' or 'duck itch'." (Also called Pelican itch in Australia) "All are caused by [zoonotic] cercariae in most freshwater bodies of water frequented by ducks and/or water birds. The cercariae penetrate the skin and cause a cercarial dermatitis. This summer is so hot even in the Northern most states that a quick plunge into the lake is certainly very appealing. We may expect to see more cases like this one."
Indeed, this is a distressing result from what would otherwise be a lovely dip in a cool lake!
An anonymous reader elaborated that "Swimmer's itch is an allergic condition that occurs when trematode cercariae, the motile and infectious stage of avian schistosomes (eg, Trichobilharzia spp.), penetrate the skin of humans. They utilize a variety of different species of birds as definitive hosts (humans are not suitable hosts), and rely on different snail species as intermediate hosts. If any, only symptomatic therapy is needed (anti-itch lotions, antihistamine), the cercariae die quickly without causing a severe trematode infection."
Marc Couturier noted "Growing up in Maine, we just called that...the result of swimming in Maine". Yikes! It's also common in northern Minnesota and Wisconsin in the United States.
I had to laugh at the Twitter (X) response from That Packer Girl 🏈 (@thatpackergirl) - "*sideyes the mergansers and snails at the family cabin*"
In the United States, swimmer's itch 'season' is mid summer. According to a post from Anoka County, Minnesota, Parks and Recreation, you can "Reduce your chances of getting severe swimmers’ itch by following these simple guidelines. Dry off as soon as you leave the water. Rub skin briskly to remove water drops before they evaporate. Be sure to dry underneath waistbands and around leg openings. Encourage children to dry off thoroughly each time they leave the water. Shower with soap and fresh water or change into dry clothes as soon as possible. Don’t wade or play in shallow water. Swimming from a raft or pontoon minimizes your exposure. Don’t feed geese and ducks near your beach. Waterfowl are an important adult host for the parasites."
I hope you all enjoy the rest of the summer!
Wednesday, August 16, 2023
Case of the Week 724
This week's case was generously donated by Dr. Nazia Nagi in New Delhi, India. She saw these 'cute' little objects (around 15 micrometers long) during her rotation in the Diarrhoeal Laboratory. The patient is a young teenager with diarrhea lasting for 15-17 days. Identification?
Saline wet mounts:Tuesday, August 15, 2023
Answer to Case 724
Answer to the Parasite Case of the Week 724: Giardia duodenalis trophozoites and cysts.
Florida Fan eloquently described the characteristic motility pattern of Giardia trophozoites: "Beautiful autumn leaves falling in the wind in a sliding side to side motion." He also notes that "Giardia trophozoites and cysts can present a little challenge to parasitologists at times. Most of us are used to see the typical kite-shaped trophozoite with its nuclei, sucking disks and flowing flagella. When these trophozoites turn sideways, we may see only ạ leafy profile, and when they stand on their tails they will look like the kid next door poking his head over the privacy fence showing only the top of the head and the two eyes. The typical ovoid cysts can float on their ends and we may observe only a spherical object with a few discernible dots for nuclei. In my practicing days, I built models of both the trophozoite and the cyst and rotated them around to show the team the different morphology when viewed at different angles. Beautiful case indeed." Thank you for the great imagery, Florida Fan!
Most people are familiar with the classic morphology of the trophozoites (and less so of the cysts), but we have to remember that not all organisms have a 'textbook' appearance. Here are the lovely images from this case:
Lastly, here is a cartoon by Dr. Nagi!
Tuesday, August 1, 2023
Case of the Week 723
This week's case was donated by Dr. Nancy Wengenack and the Mycology lab at Mayo Clinic. These objects were found in a fungal culture for dermatophytes (lactophenol blue stain). What are they, and what is their significance?